CANDIDIASIS(CAUSES,SYMPTOMS,PREVENTION & TREATMENT)
WHAT IS CANDIDIASIS?
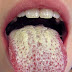
 CANDIDIASIS is a fungal infection due to any type of Candida (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it is commonly called a yeast infection. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Less commonly the penis may be affected, resulting in itchiness. Very rarely, the infection may become invasive spreading throughout the body, resulting in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts of the body affected.
CANDIDIASIS is a fungal infection due to any type of Candida (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it is commonly called a yeast infection. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Less commonly the penis may be affected, resulting in itchiness. Very rarely, the infection may become invasive spreading throughout the body, resulting in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts of the body affected.
More than 20 types of Candida can cause infection with Candida albicans being the most common.
Infections of the mouth are most common among children less than one month old, the elderly, and those with weak immune systems. Conditions that result in a weak immune system include HIV/AIDS, the medications used after organ transplantation, diabetes, and the use of corticosteroids. Other risks include dentures and following antibiotic therapy. Vaginal infections occur more commonly during pregnancy, in those with weak immune systems, and following antibiotic use. Risk for widespread infection includes being in an intensive care unit, following surgery, low birth weight infants, and those with weak immune systems.
2.Vaginal burning with intercourse or urination
3.Vaginal discharge resembling cottage cheese (thick and white) that is odorless
4.Vagina Rash
5.Vagina Soreness
6.Vagina Pain
7. Unpleasant Vagina odor?
WORRY NO MORE THE SAVIOR IS HERE

WHAT CAUSES VAGINAL YEAST INFECTIONS?
The Candida genus of yeast is a naturally occurring microorganism in the vaginal area. Its growth is kept in check by the lactobacillus bacteria. However, these bacteria can’t work effectively if there’s an imbalance in your system. This leads to an overgrowth of yeast, which causes the symptoms of vaginal yeast infections.
Most yeast infections are caused by a specific kind of yeast called Candida albicans. These yeast infections are easily treatable. If you’re having recurring yeast infections or problems getting rid of a yeast infection with conventional treatment, then a different version of Candida might be the culprit. A lab test can let your doctor know which type of Candida you have.
The imbalance that allows the overgrowth of yeast to happen can be due to:
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF A VAGINAL YEAST
INFECTION?
Vaginal yeast infections have a common set of symptoms. Usually the length of time your yeast infection is left untreated has a direct impact on how severe your symptoms are.

Frequent
symptoms include:
WHAT IS THE BEST WAY TO PREVENTION VAGINAL YEAST INFECTION?
Each yeast infection is different, so your nutritionalist will suggest a prevention that’s best for you. Prevention are generally determined based on an infection’s severity.
Simple infections
For simple yeast infections, your doctor will usually prescribe the following treatment(s):
Women with simple yeast infections should follow up with their doctor to make sure the medicine worked. A follow-up will also be necessary if your symptoms return within two months.
Complicated infections
Certain types of Candida will not respond to normal treatment and will require a more aggressive course of action. If you meet one of the following criteria, your Nutritionist will more than likely prevent your yeast infection as if it were a severe or complicated case.
Possible prevention for severe or complicated yeast infections include:
What natural and alternative solutions are available?
You can treat vaginal yeast infections with natural remedies if you would like to avoid taking prescription medication. These are some popular natural remedies:
How do you prevent vaginal yeast infections?
In many cases, you may know exactly what led to your yeast infection. For example, some women experience these infections every time they take antibiotics. By recognizing your own risk factors, you can prevent future infections.
HOW TO PREVENT CANDIDA INFECTION
Here are some common methods of prevention. Most are targeted at avoiding bacteria growth near the vagina: